Mix² RNA-Seq Data Analysis Software
Model
Fragment bias in RNA-Seq poses a serious challenge to the accurate quantification of gene isoforms. Mix² makes no assumptions about coverage bias but fits for each gene isoform a mixture model to the data (Fig. 1). Mix² can therefore, for instance, accurately represent the 5’ bias, as shown in Fig. 1 (a and b), whereas Cufflinks is restricted to the uniform distribution (Fig. 1c).
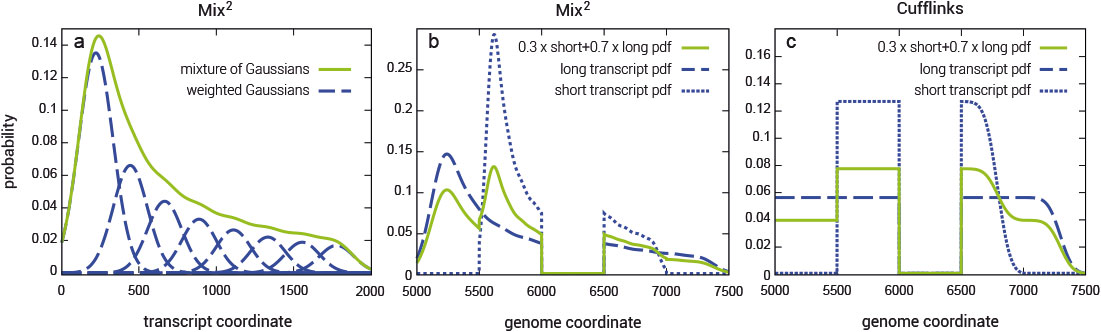
Figure 1 | Exemplary representation for positional fragment bias over a 2000 bps transcript modeled with a mixture of 8 normal distributions. (a) the green curve shows the combined probability density function over the whole transcript, while the blue curves show the individual mixture distributions. (b) and (c) panels display fragment distributions in a locus with two transcripts sharing one junction, as modeled by Mix² or Cufflinks. Long and short transcripts start at 5000 and 5500 bp from the beginning of the locus, and are 2000 and 1000 bp long, respectively. The junction spans the 6000 – 6499 bp region.
The Mix² software yields accurate isoform quantification from RNA-Seq data
Implementation and run-time performance
The Mix² software runs as a 64-bit Linux command line tool. For an up-to-date list of supported distributions please refer to the User Guide of the Mix² software.
| Mix² | Cufflinks w/o bias correction | Cufflinks with bias correction | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Min | GB | Min | xRT | GB | xMEM | Min | xRT | GB | xMEM |
| Avg (UHR) | 7 | 1.26 | 34 | 4.9 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 542 | 77.4 | 1.32 | 1.05 |
| Avg (HBR) | 5 | 1.02 | 32 | 6.4 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 536 | 107.2 | 1.22 | 1.20 |
Table 1 | Memory usage and average run-time statistics on the MAQC UHR and HBR datasets. Min stands for run-time in minutes, GB for memory usage in gigabytes. xRT and xMEM are the factors by which run-time and memory usage increases, respectively, in comparison to Mix².
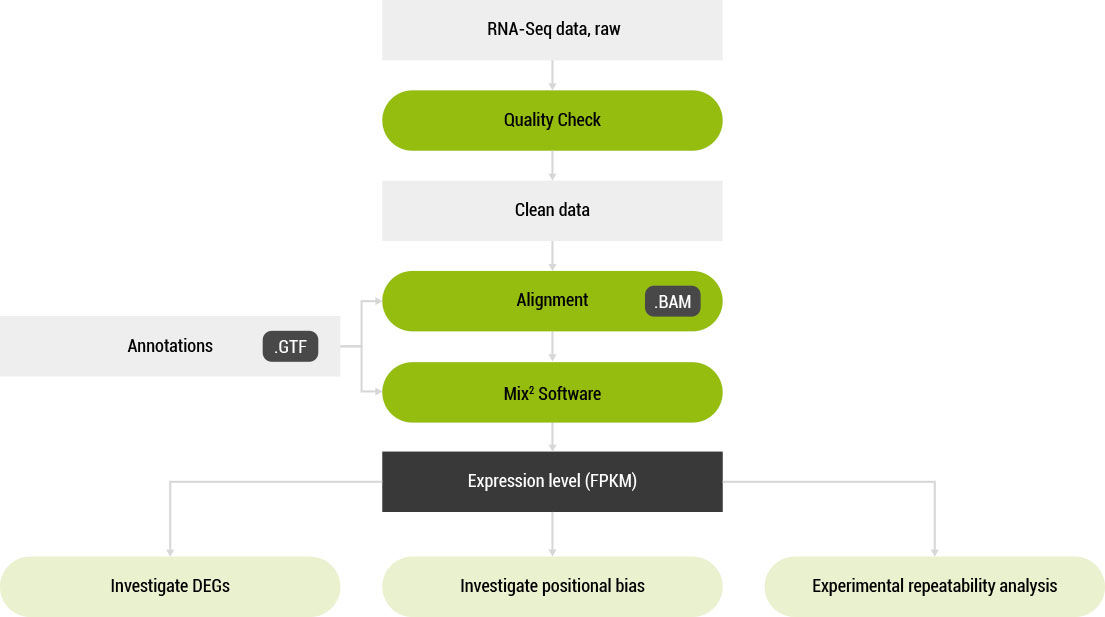
Mix² Workflow